Directives¶
List of available directives with examples.
Namespace¶
Namespace directive for defining namespaces. Every child will be in this namespace.
Attention
Type directive can override the parent.
Type¶
Type directive for C# object types:
- class
- interface
- struct
Options¶
- nonamespace - hide namespace above type.
- parent - explicit name of parent to override.
- noindex - don’t add the index for this object.
Caution
Declared type will be as parent for their childrens (except types).
Usage¶
Defining of types¶
.. type:: public class CSharpClass
:nonamespace:
Example of type without namespace text above.
.. type:: public class CSharpGeneric<T,T2>
Example of generic type.
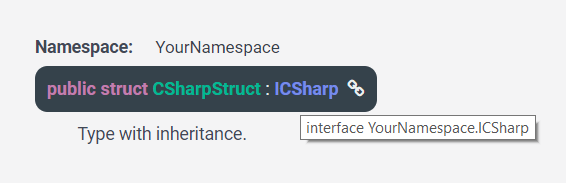
.. type:: public struct CSharpStruct : ICSharp
Example of type with inheritance.
.. type:: public interface ICSharp
Example text with reference on :type:`CSharpClass`.
Warning
Type without modificators will be equal to private.
Result¶
- public class CSharpClass¶
Example of type without namespace text above.
- public class CSharpGeneric<T, T2>¶
Example of generic type.
- public interface ICSharp¶
Example text with reference on CSharpClass.
Tip
Also pay your attention how the link looks like.
End-Type¶
Directive for ending current parent type.
Usage¶
.. type:: public class CSharpClass
This type is now a parent for it childrens.
.. variable:: public int ID
Link on this variable equals: CSharpClass.ID
.. end-type::
.. variable:: public int AnotherID
Now, after ending of the type, link on this variable equals: AnotherID
Note
This directive was helpful for this documentation, where no need in parent types.
Variable¶
Variable directive for C# variables.
Options¶
- noindex - don’t add the index for this object.
Usage¶
Defining of variable¶
.. variable:: public int IntVar
Example of default variable.
.. variable:: public const string CONST_STR
Example of default variable with additional modifiers.
.. variable:: public CSharpClass ClassVar
Example of variable with some reference type.
.. variable:: public DateTime Now = DateTime.Now
Example of variable with default value.
.. variable:: public event OnStart OnStartEvent
Example of variable with reference on method.
Example text with reference on :var:`IntVar`.
Result¶
- public int IntVar¶
Example of default variable.
- public const string CONST_STR¶
Example of default variable with additional modifiers.
- public CSharpClass ClassVar¶
Example of variable with some reference type.
- public DateTime Now¶
- Value:DateTime.Now
Example of variable with default value.
Example text with reference on IntVar.
Property¶
Property directive for C# properties.
Options¶
- noindex - don’t add the index for this object.
Usage¶
Defining of property¶
.. property:: public int IntProp { get; set; }
Example of property with "get; set;" accessors.
.. property:: public CSharpStruct StrProp { get; private set; }
Example of property with private set accessor.
.. property:: public bool BoolProp { get; }
Example of property only with one accessor.
Example text with reference on :prop:`StrProp`.
Result¶
- public int IntProp { get; set; } ¶
Example of default property with “get; set;” accessors.
- public CSharpStruct StrProp { get; private set; } ¶
Example of property with private set accessor.
- public bool BoolProp { get; } ¶
Example of property only with one accessor.
Example text with reference on StrProp.
Method¶
Method directive for C# methods.
Options¶
- param() - description of parameter with ordinal id in brackets (not necessary).
- returns - description of return value (not necessary).
- noindex - don’t add the index for this object.
Important
Parameter ordinal id start from 1.
Usage¶
Defining of method¶
.. method:: public void ExampleMethod()
Example of method without return value and without any parameter.
.. method:: public string GetString()
:returns: Some string
Example of method with some return value and description of it.
.. method:: public delegate void OnStart()
Example of method with additional modifiers.
.. method:: public void ParamMethod(int arg1, bool[] arg2, ref CSharpClass arg3, params bool[] args)
:param(1): Description of the first parameter.
:param(2): Description of the second array parameter.
:param(3): Description of the third reference parameter.
:param(4): Description of the params parameter.
Example of method with different types of parameters.
.. method:: public CSharpStruct(string someString)
Example of method as constructor.
Example text with reference on :meth:`GetString`.
Result¶
- public void ExampleMethod()¶
Example of method without return value and without any parameter.
- public string GetString()¶
- Returns:Some string
Example of method with some return value and description of it.
- public delegate void OnStart()¶
Example of method with additional modifiers.
Note
You can reference on this method, as in example.
- public void ParamMethod(int arg1, bool[] arg2, ref CSharpClass refArg, params bool[] args)¶
Example of method with different types of parameters.
arg1:Description of the first parameter.arg2:Description of the second array parameter.refArg:Description of the third reference parameter.args:Description of the params parameter.
- public CSharpStruct(string someString)¶
Example of method as constructor.
someString:And again some string.
Example text with reference on GetString.
Attention
If you specify a non-existing identifier of the parameter, you will get an error.
Enum¶
Enum directive for C# enumerables.
Options¶
- values - list of values separated by space (necessary).
- val() - description of the value with ordinal id in brackets (not necessary)
- noindex - don’t add the index for this object.
Important
Value ordinal id start from 1.
Usage¶
Defining of enum¶
.. enum:: public enum MoveTypes
:values: Idle Walk Run Milos
:val(1): Idle state.
:val(2): Relaxing walk.
:val(3): Run Forest, Run!
:val(4): Ricardo Milos dance.
Example of default enum.
Example text with reference on :enum:`MoveTypes`.
Result¶
- public enum MoveTypes¶
Example of default enum.
Values:Idle, Walk, Run, MilosIdle:Idle state.Walk:Relaxing walk.Run:Run Forest, Run!Milos:Ricardo Milos dance.
Example text with reference on MoveTypes.
Attention
If you specify a non-existing identifier of the value, you will get an error.
Attention
You must assign the values, or you will get an error.